STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS ON NEUROHUMORAL PARAMETERS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEART FAILURE
Aim. To study the effectiveness of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists-spirinolactone and eplerenone on neurohumoral parameters in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF).
Methods. 100 patients with ischemic heart failure with II and III FC heart failure were examined initially and after 6 months of treatment. To assess the comparative effectiveness of AMRK patients were divided into 2 groups: the first group (I) consisted of 54 patients were taken for 6 months against the background of standard therapy-spirinolactone; the second group (II) -46 patients eplerenone.
Results. The result of the therapy with spirinolactone in patients with II FC, the AL content
decreased by 26.6% (p<0.001) from the initial values, and the content of NA decreased by
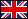
20.2%. In patients with III FC, decrease only in the AL level by 20.2% (p<0.05).
The level of NA decreased by 10.9% from the initial value, which was statistically
insignificant. The results eplerenone therapy showed that in this group of patients
significantly reduced the content of neurohormones in the blood of patients with CHF as
FC II and FC III. As a result of the therapy, patients with FC II had a significant decrease in
AL content by 28.4% (p<0.01), and by 24.6% (p<0.01) from the baseline. In patients with
CHF FC III, the Al content decreased by 32.1%, and NA by 19.8% (p<0.05) from
the baseline. The results of the comparative effectiveness of spirinolactone and eplerenone
showed that the effectiveness of complex therapy on the level of neurohormones is almost
similar in both groups in patients with FC II. However, patients with FC III have a clear
superiority of complex therapy with eplerenone than with spirinolactone.
Сonclusion. Thus, in complex therapy with the use of AMCR in patients with CHF, eplerenone more significantly reduced the level of neurohormones, both in patients with II and III FC CHF.