ACUTE HEMODYNAMIC EFFECT OF A NOVEL MULTI-SITE, MULTI-POINT BIVENTRICULAR PACING CONFIGURATION
Background: Biventricular pacing (BVP) from multiple left ventricular (LV) sites may augment the hemodynamic effect of cardiac resynchronization therapy by engaging a greater mass of the myocardium.
Purpose: To evaluate the acute hemodynamic effect of a novel multi-site, multi-point BVP configuration.
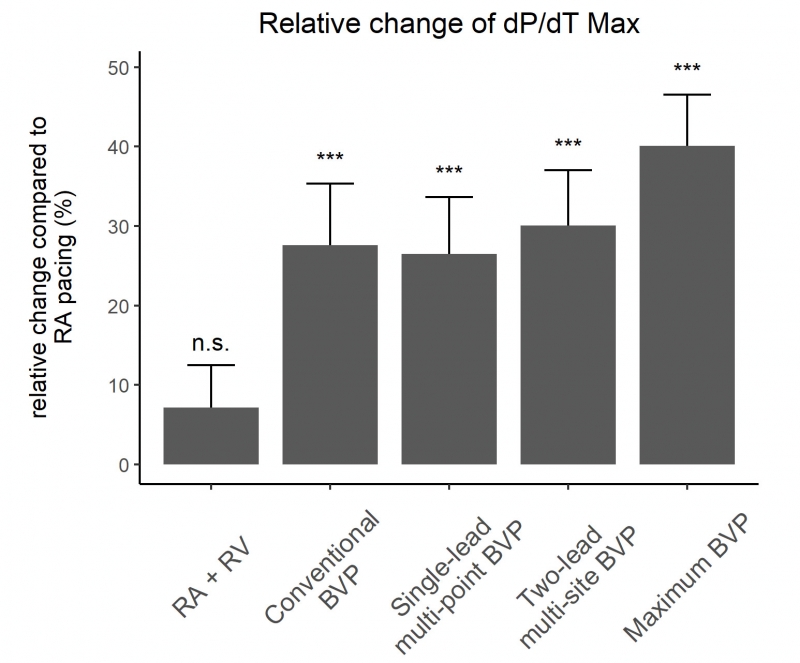
Methods: The study investigated 18 patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and left bundle-branch block during implantation of a BVP device (age: 59 ± 14 years, LVEF: 27 ± 6%, QRS: 171 ± 16 ms). Conventional leads were placed in the right atrium (RA) and ventricle (RV), one quadripolar LV lead (Quartet, Abbott, Abbott Park, IL, USA) was positioned in the posterolateral and another one in the lateral or anterolateral coronary vein. Bipoles of the leads were connected into separate external cardiac stimulators. LV dP/dT was measured with a micromanometer-tipped catheter during RA pacing above sinus rate and five atrioventricular sequential pacing configurations at the same rate: 1.) RA+RV, 2.) RA + RV + distal bipole of the LV lead with greater dP/dT („conventional BVP“), 3.) RA + RV + distal and proximal bipoles of the LV lead with greater dP/dT („single-lead multi-point BVP“), 4.) RA + RV + distal bipoles of both LV leads („two-lead multi-site BVP“), and 5.) sequential pacing RA + RV + all bipoles of both LV leads interconnected to a mesh („maximum BVP“).
Results: Compared to RA pacing, LV dP/dT was significantly greater during all BVP pacing configurations, but not during RA-RV pacing (Figure 1). In addition, dP/dT was significantly greater during “maximum BVP” compared to conventional BVP (p=0.05).
Conclusion: Compared to RA pacing and conventional BVP, the greatest increase in LV contractility was achieved with a novel multi-site, multi-point “maximum BVP” configuration. These preliminary findings provide a rationale for designing new approaches to BVP.