LACTATE IN REFRACTORY OUT-OF-HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST. THE PRAGUE OHCA STUDY SUBANALYSIS.
INTRODUCTION
The prognosis of patients suffering refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) remains serious despite the implementation of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR). Serum lactate (s-Lac) level is an easily measured parameter reflecting the severity of hypoperfusion and tissue hypoxia. We hypothesized, that early lactate levels might be useful in predicting the outcome after OHCA.
METHODS
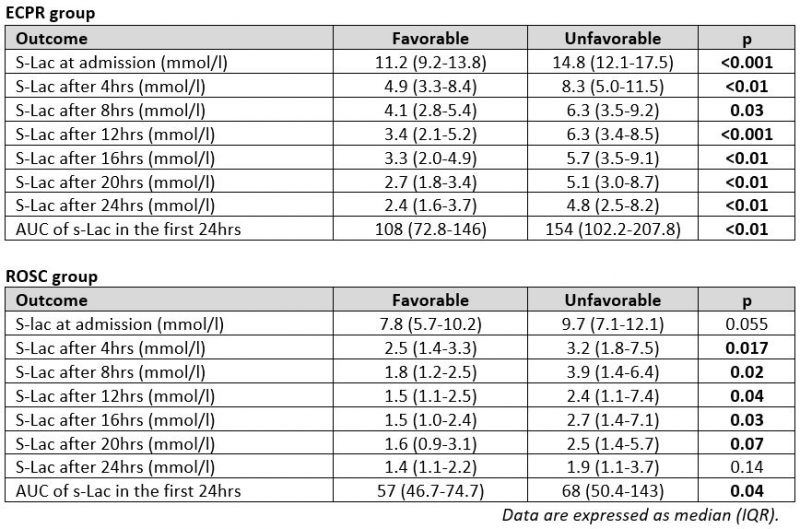
This is a post-hoc analysis of the biochemical data from the randomized clinical trial “Prague OHCA study” comparing invasive (ECPR) and standard approaches in refractory OHCA patients. Patients, who have undergone ECPR (“ECPR group”) treated with veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and patients, in whom the prehospital ROSC has been achieved (“ROCS group”), were analyzed separately and irrespective of randomization schema. The s-Lac level was measured at admission to the hospital and then repeatedly every 4 hours during the first 24 hours. Based on the values, the total area under the curve (AUC) of s-Lac in the first 24hours was calculated for every patient. The best Cerebral Performance Category (CPC) score reached during the 180 days long follow-up after the OHCA event was used to determine favorable (F; CPC 1, 2) and unfavorable outcome (UF; CPC 3, 4, 5).
RESULTS
Out of 92 patients in the ECPR and 82 patients in the ROSC group, F outcome was reached in 24 (26%) and 48 (59%) subjects, respectively. The AUCs of s-Lac levels in the first 24hours were significantly different between F and UF patients in both ECRP and ROSC groups. More details are in the Table.
CONCLUSION
The AUCs of s-Lac levels measured during the first 24 hours after refractory OHCA are significantly different between patients with F and UF long-term neurological outcome regardless the use of ECPR methods.