RIGHT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION ASSESSMENT USING GATED BLOOD-POOL SPECT VENTRICULOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED HEART FAILURE
Purpose: Assessment of right ventricular (RV) function and volumes is critical for planning of advanced heart failure (HF) therapies, but it is often difficult and imprecise, particularly in HF patients after LVAD implantation. The goal of the study was to test performance of quantitative 3-dimensional gated blood-pool single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging of the RV using novel high-resolution SPECT camera.
Methods: We examined 21 patients with advanced HF (age 61±11 years, LV EF 28±16%, 76% males, BMI 28±4 kg/m2, 4 patients with LVAD HeartMate III). 30 minutes after injection of stannous pyrophosphate (Technestan PYP), erythrocytes were in-vivo labeled by intravenous injection of 740 MBq 99mTc isotope (radiation dose 5-6 mSv). The heart chambers were imaged using D-SPECT camera (Spectrum Dynamics, Israel) with Cd-Zn-Te detector. Volume analyses from 3D reconstructed chambers were performed using semiautomatic plug-in software (QBS Cedars-Sinai, USA). Data acquisition and analysis were performed twice to assess reproducibility.
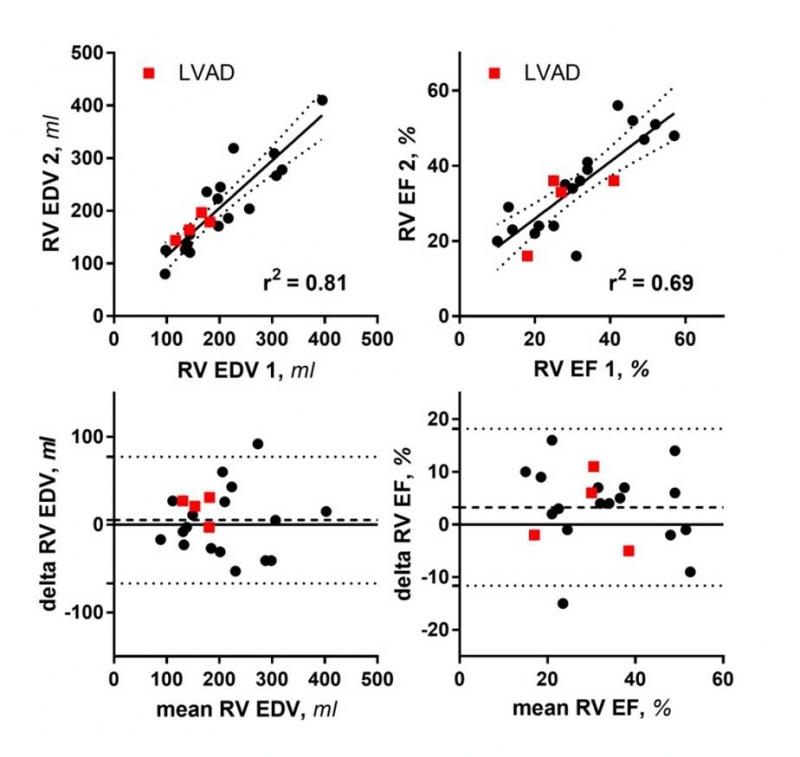
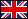
Results: Imaging was successful even in subjects with LVADs, although in 2 patients with HMIII device we experienced intermittent interference with surface ECG gating, requiring cable repositioning. Acquisition time was set for 8 minutes in all subjects. Data processing required no (in 2/3 of subjects) or minimal manual intervention. As shown in the figure, RV end-diastolic volume (EDV) and ejection fraction (EF) displayed very good correlation (R2: 0.69-0.81). In Bland-Altman plots, both measures had only minimal bias, and acceptable confidence limits. Reproducibility in LVAD patients was similar to non-LVAD group.
Conclusion: Gated blood-pool SPECT assessment of the right ventricular function is fast and reproducible method, even in HF patients with severe RV dysfunction or after LVAD implantation.