SECONDARY PREVENTION OF MAJOR ADVERSE CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS IN PATIENTS WITH PLATELET MEMBRANE GLYCOPROTEIN VI POLYMORPHISM
Z. Moťovská, P. Widimský, I. Kocianová, R. Petr, D. Odvodyová, M. Fisherová, S. Katina (Praha, Bratislava, SR)
Topic: Secondary prevention
Type: Presentation - doctors, 19th CSC Annual Congress
| Odds Ratio | 95 % Confidence Interval | P-Value | |
| Death | 2.367 | 0.143 to 39.093 | 0.547 |
| Myocardial Infarction (MI) | 0.586 | 0.063 to 5.474 | 0.639 |
| Re-Intervention | 0.946 | 0.304 to 2.943 | 0.923 |
| Death/Myocardial Infarction/Reintervention | 1.100 | 0.258 to 4.697 | 0.896 |
Methods Long-term follow up was investigated in 105 consecutive patients who were affected by a premature MI. Of these patients 31.4% were carriers of the C-allele.
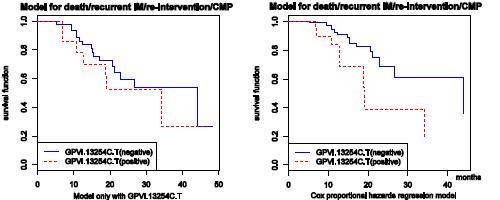
Results The follow-up period was mean(SD) 19.0(10.8) months. Univariate analysis did not find significant differences in the occurrence of MACE between GP VI 13253C allele carriers and non-carriers of the C-allele (Table). Multivariate Cox's regression was performed. Variables included in the model were age,sex,known cardiovascular risk factors,LVEF<50%,NYHA >I, aspirin and statin therapy. GP VI 13254C allele was recognized as an independent risk factor for recurrence of MACE despite secondary prevention therapy with aspirin and statin (adjusted odds ratio 5.203 (95%C.I. 1.284 to 21.084, p = 0.021)(Figure).
Conclusion GP VI 13254C/T is a frequent genetic variant in patients with premature MI. Secondary prevention with aspirin and statin therapy is insufficient to prevent recurrence of MACE in C-allele carriers.