INTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS DURING PULSED ELECTRIC FIELD ABLATION IS LINEARLY DEPENDENT ON THE NUMBER OF APPLICATIONS
Background: Pulsed electric field (PEF) has emerged as a promising energy source for the treatment of patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). However, data are scarce regarding the in-vivo effect of PEF energy on erythrocytes during AF ablation procedures.
Objective: To quantify the impact of pulsed electric field energy on erythrocyte damage during AF ablation by assessing specific hemolytic biomarkers.
Methods: A total 60 patients (age: 66±9 yrs, males: 72%) with persistent AF underwent PEF ablation using a Faradrive catheter. Ablation beyond PVI was performed at the operator’s discretion. The control group had 10 patients who underwent PVI using a cryoballon catheter. Peripheral venous blood was sampled for assessing the plasma levels of free haemoglobin (free Hb), direct bilirubin, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatinine, and haemoglobin (Hb) before, immediately after the ablation, and on the next day.
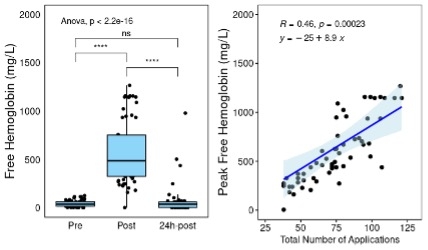
Results: Following the PEF ablation (duration: 79±28 min, number of applications: 73±23, PVI only: 27%), free Hb, LDH, and direct bilirubin significantly increased, from 47±34 to 628±432 mg/L, from 3±1 to 5±1 kat/L, and from 14±8 to 34±21 mol/L, respectively (all P <0.0001) while their change in the control group was from 36±28 to 226±96 mg/L, from 3±1 to 4±1 kat/L, and from 11±2 to 17±8 mol/L, respectively (all P <0.01). The periprocedural dynamics of free Hb and a correlation between the peak free Hb levels and the total number of PEF applications are depicted in Figure. No significant changes in total Hb and creatinine levels were observed.
Conclusion: Catheter ablation of AF using PEF energy is associated with significant intravascular hemolysis that is linearly related to the total number of PEF applications. However, the critical amount of PEF energy that may cause kidney injury in susceptible patients remains to be investigated.