STEREOTACTIC BODY RADIOTHERAPY FOR REFRACTORY VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA: THE OVERALL CZECH EXPERIENCE
Background: Catheter ablation (CA) is a well-established treatment strategy for the management of drug-refractory ventricular tachycardia (VT) in patients with structural heart disease. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) was proposed recently as a treatment option for cases of failed CA.
Purpose: This study reports overall experience with the SBRT from two Czech centers.
Methods: Since 2014, we enrolled consecutive patients who underwent at least one prior CA for recurrent scar-related VT and had subsequent VT recurrences due to inaccessible substrate. Single-session SBRT was performed and a dose of 25 Gy was delivered.
Results: The study investigated 33 patients (3 women) with a mean age of 66 ± 9 years. Underlying heart disease was ischemic (58%) and nonischemic (39%) cardiomyopathy; one patient had large cardiac fibroma. The mean left ventricular ejection fraction was 31 ± 8%. Seventy-six percent of patients were on amiodarone.
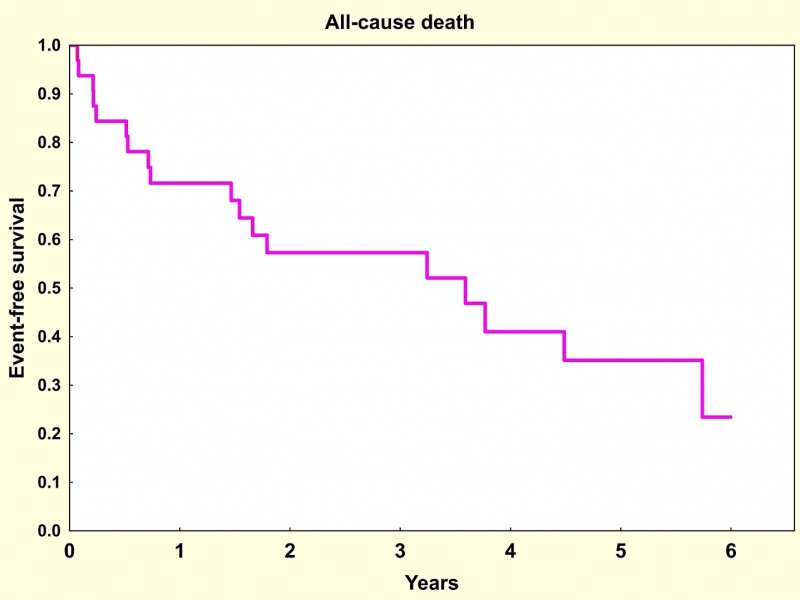
Seventeen (52%) patients died during the mean follow up of 29 ± 23 months mainly due to the progression of heart failure (Figure 1). One patient died due to bleeding associated with esophagopericardial fistula that developed 9 months after SBRT.
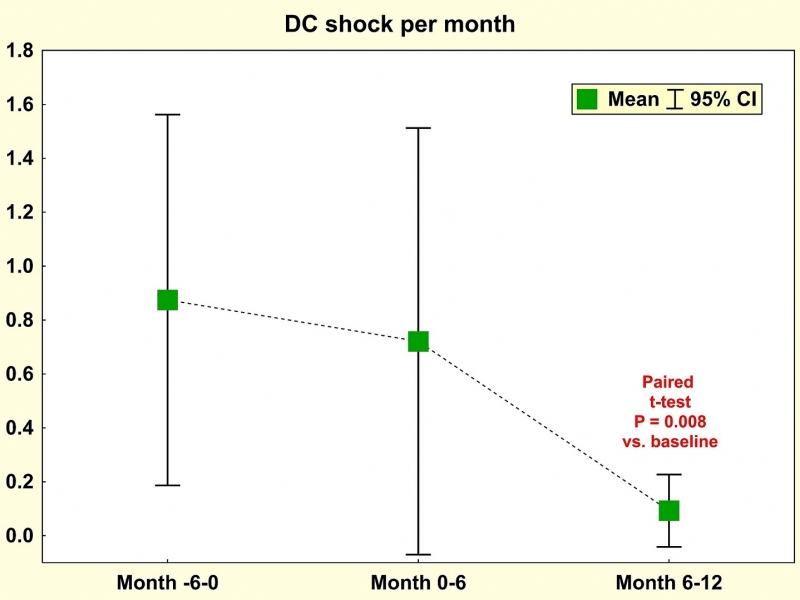
Overall, the number of DC shocks after a single procedure decreased significantly from 0.9 ± 1.9 per month in the period of 6 months before SBRT to 0.1 ± 0.3 per month in the period of 6-12 months after SBRT (P=0.008, Figure 2). However, 14 patients (42%) had to undergo additional CA due to VT recurrences at a mean interval of 13 ± 14 months after SBRT.
Conclusions: SBRT in patients with refractory VT is feasible but the long-term mortality after the procedure is high and reflects mainly the severity of the underlying disease. The treatment effect of SBRT is delayed and additional CA is often necessary for VT suppression.